What happens during your first consultation?
Listening to all your health concerns and gathering information
If you have never had an holistic treatment before, you will probably be pleasantly surprised by the experience. In my consultations, clients have often said that they feel it's the first time that someone's really listened to them and taken their symptoms seriously. This is probably because, in holistic healing, every aspect of your health is important, and all the symptoms that you choose to tell me about, no matter how minor, will be taken into account when I treat you. Seemingly unrelated symptoms can point in the direction of treatment. This initial consult typically takes from one and a half to two hours.
Taking full details of your health history
In your first consultation, I would usually start by asking about your main complaint. I would then ask you a series of questions about other symptoms that you may or may not have. These would be symptoms that I think may be related in some way to your main complaint. If you have already submitted the intake forms online, I will have already studied these and as questions specific to the information provided. During this process, I would also ask you about any major illness that you've had throughout your life.
I will also request any recent laboratory blood work you may have done. Also included in the initial consult fee are various labs which test for common nutrient deficiencies, such as Vitamin D, Red Blood Cell (not serum) Magnesium, Zinc, Vitamin B12, Folate, and more...
This process, together with my observations about your complexion, general manner and appearance, would enable me to start forming my diagnosis. All of the on-line presubmitted forms will have already given me an idea of how to conduct the questioning during this initial consult. Request Appointment Online
Integrative Medicine
In addition to Functional Medicine methods I also make full use of Eastern medicianl herbals and provide treatment plans that are truly integrated. My approach is a multi-dimensional one in which all levels are addressed in order to facilitate true healing using a variety of natural medicine modalities and the most cutting-edge functional medicine investigations. On your follow-up consult you receive a 20 page report tailored to your specific imbalances and health issues. You also receive a customized Health Improvement Plan designed for your health needs. This Consult Summary will also include nutritional and lifestyle recommendations necessary to get you to optimal health! Both the intake and the follow-up consults are an hour long. The follow-up is recorded and sent to you post-session.
labs included(mAY VARY DEPENDING ON INDIVIDUAL NEEDS AND CLINICAL PRESENTATION - all included in initial consult fee):
Blood Analysis and Health Improvement Plan
Fasting Required: Yes 10-12 hours
Specimen: Blood
Lab: Labcorp
Results: 3-5 business days
Note: Result turnaround times are an estimate and are not guaranteed. Our reference lab may need additional time due to weather, holidays, confirmation/repeat testing, or equipment maintenance.
Description: 18 most important tests people over 40 should take each year.
Tests Included
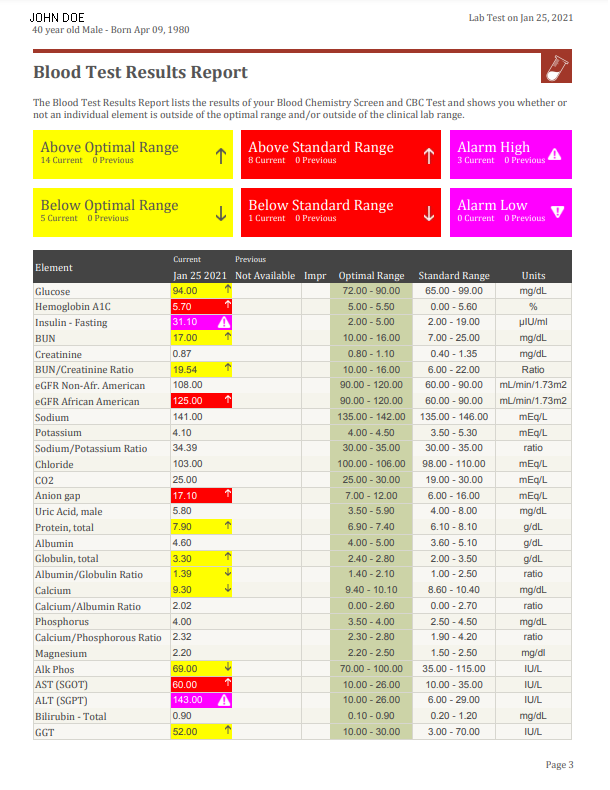
Comprehensive Wellness Profile (CWP) Over 50 individual laboratory tests screen for cardiovascular risk, major organ function, anemia, diabetes, infection, blood disease, thyroid disorders and other indications of illness. This panel is routinely ordered as a part of an annual exam. It includes:
Lipids: This is a group of simple blood tests that reveal important information about the types, amount and distribution of the various types of fats (lipids) in the bloodstream. Includes Total Cholesterol, HDL (good) Cholesterol, LDL (bad) Cholesterol, Risk Ratio (good to total), and Triglycerides.
Complete Blood Count (CBC): It is a blood test that checks hemoglobin, hematocrit, red blood cells (RBC), white blood cells (WBC), and platelets. Used as a broad screening test to check for such disorders as anemia, infection, and many other diseases. Changing levels of red or white blood cells can indicate disease or infection and are very helpful in a health screening.
Fluids and Electrolytes: Electrolytes are minerals in your body that have an electric charge. They are in your blood, urine and body fluids. Maintaining the right balance of electrolytes helps your body's blood chemistry, muscle action and other processes. Sodium, potassium, chlorine, and carbon dioxide are all electrolytes. You get them from the foods you eat and the fluids you drink. Levels of electrolytes in your body can become too low or too high. That can happen when the amount of water in your body changes, causing dehydration or overhydration. Causes include some medicines, vomiting, diarrhea, sweating or kidney problems. Problems most often occur with levels of sodium, potassium or calcium. It includes: Chloride, Potassium, Sodium and Carbon Dioxide.
Liver: The liver panel includes several blood tests measuring specific proteins and liver enzymes in the blood. This combination of blood tests is designed to give you a complete picture of the state of your liver and help detect liver disease and measure potential liver damage. Some of the blood tests are associated with the integrity of the liver cells (i.e. ALT), some with liver function (i.e. albumin) and some with disease linked to the biliary system (i.e. alkaline phosphatase). Includes: Albumin, Alkaline Phosphatase, Alanine Transaminase (ALT or SGPT), Aspartate Transaminase (AST or SGOT), Total Bilirubin, Total Protein, LDH, Total Globulin, Albumin/Globulin Ration and GGT.
Kidney: This basic metabolic panel is a group of blood tests that provides information about your body's metabolism. This test is done to evaluate kidney function, blood acid/base balance, blood sugar levels. It includes Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN), Creatinine, BUN/Creatinine Ratio, eGFR, and Uric Acid.
Glucose: Changes in blood glucose are a good indicator of metabolic function and can help detect diseases like diabetes mellitus. Since diabetes is the most common cause of kidney disease in adults, it is important to monitor for this disorder when evaluating kidney function.
Fasting Insulin: Insulin is the hormone that enables cells to take in glucose. Without insulin, glucose can't get into the cells and it stays in the bloodstream. With too little insulin, blood sugar remains higher than normal (a condition known as hyperglycemia) and cells can't get the energy they need. With too much insulin, blood sugar decreases (hypoglycemia), causing symptoms such as sweating, trembling, lightheadedness, and in extreme cases, shock.
Mineral and Bone: In addition to its mechanical functions, the bone is a reservoir for minerals (a "metabolic" function). The bone stores 99% of the body's calcium and 85% of the phosphorus. It is very important to keep the blood level of calcium within a narrow range. If blood calcium gets too high or too low, the muscles and nerves will not function. In times of need, for example, during pregnancy, calcium can be removed from the bones. It includes: Total Iron, Calcium, and Phosphorus. Also Magnesium, an important mineral involved in over 300 vital chemical pathways in the body. Zinc is essential for wound-healing, immune function, nails and hair and more.
Vitamin B12: Vitamin B12 is a nutrient that helps keep the body's nerve and blood cells healthy and helps make DNA, the genetic material in all cells. Vitamin B12 also helps prevent a type of anemia called megaloblastic anemia that makes people tired and weak. Two steps are required for the body to absorb vitamin B12 from food: First, hydrochloric acid in the stomach separates vitamin B12 from the protein to which vitamin B12 is attached in food. After this, vitamin B12 combines with a protein made by the stomach called intrinsic factor and is absorbed by the body.
Vitamin B9 (Folate): Vitamin B9, also called folate or folic acid, is one of 8 B vitamins. Folic acid is crucial for proper brain function and plays an important role in mental and emotional health. It aids in the production of DNA and RNA, the body's genetic material, and is especially important when cells and tissues are growing rapidly, such as in infancy, adolescence, and pregnancy. Folic acid also works closely with vitamin B12 to help make red blood cells and help iron work properly in the body.
Vitamin D, 25 Hydroxy: Also known as the "sunshine vitamin" because the body manufactures the vitamin after being exposed to sunshine. Ten to 15 minutes of sunshine 3 times weekly is enough to produce the body's requirement of vitamin D. Needed for strong bones and teeth, Vitamin D helps your body absorb the amount of calcium it needs. It also has other roles in the body, including modulation of cell growth, neuromuscular and immune function, and reduction of inflammation. There are associations between low Vitamin D levels and peripheral vascular disease, certain cancers, multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile diabetes, Parkinson's, and Alzheimer's disease.
Iron and Total Iron Binding Capacity - Total iron binding capacity (TIBC) is a blood test to see if you have too much or too little iron in your blood. Iron moves through the blood attached to a protein called transferrin. This test helps your health care provider know how well that protein can carry iron in your blood. This is also used to identify different types of anemia.
Ferritin: Composed of iron and protein, Ferritin is a storehouse for iron in the body. Measurement provides an accurate picture of how much iron you have available in reserve. Low Ferritin is a sign of iron deficiency. Ferritin is high with inflammation, infection, liver disease, iron overload, certain amends, and certain cancers (leukemia and lymphoma).
TSH: The best way to initially test thyroid function is to measure the TSH level in a blood sample. A high TSH level indicates that the thyroid gland is failing because of a problem that is directly affecting the thyroid (primary hypothyroidism). The opposite situation, in which the TSH level is low, usually indicates that the person has an overactive thyroid that is producing too much thyroid hormone (hyperthyroidism). Occasionally, a low TSH may result from an abnormality in the pituitary gland, which prevents it from making enough TSH to stimulate the thyroid (secondary hypothyroidism). In most healthy individuals, a normal TSH value means that the thyroid is functioning normally.
Free T3: This test is used to evaluate thyroid function. It is primarily used to diagnose hyperthyroidism. It is also used to assess abnormal binding protein disorders and to monitor thyroid replacement and suppressive therapy .
Free T4: This test is used to evaluate thyroid function in individuals who may have protein abnormalities that could affect total T4 levels. It is used to evaluate thyroid function and monitor replacement and suppressive therapy.
TPO Abs: The TPO gene provides instructions for making an enzyme called thyroid peroxidase. This enzyme plays a central role in the function of the thyroid gland. Thyroid peroxidase assists the chemical reaction that adds iodine to a protein called thyroglobulin, a critical step in generating thyroid hormones. Thyroid hormones play an important role in regulating growth, brain development, and the rate of chemical reactions in the body (metabolism). Antibodies to this enzyme is indicative of autoimmune thyroiditis.
TAA: This test helps to detect possible thyroid problems. Thyroglobulin is a protein that is normally confined to the thyroid gland. It is the source of the thyroxine and triiodothyronine hormones in the body. The presence of autoantibodies to thyroglobulin can lead to the destruction of the thyroid gland. Such antibodies are more likely to appear after trauma to, or inflammation of, the thyroid gland. is one of the acute phase proteins that increase during systemic inflammation.
DHEA-S: Dhea-s is the child hormone of DHEA and serves as a building block for making the male sex hormone testosterone and the female sex hormone estrogen. DHEA-s concentrations peak after puberty and then the levels tend to decline with age. Adrenal tumors, cancers, and adrenal hyperplasia can lead to the overproduction of DHEA-s. The rate of secretion of DHEA-S into the blood stream is only slightly more than the rate observed for DHEA.
Hemoglobin A1C: This non-fasting test, also known as A1c, HbA1c, Glycohemoglobin, or Glycated hemoglobin, indicates how well you have controlled your diabetes over the last few months. Even though you may have some very high or very low blood glucose values, Hemoglobin A1C will give you a picture of the average amount of glucose in your blood over that time period. While the Hemoglobin A1C is the standard tool to determine blood sugar control for patients with diabetes, it is not a substitute for daily, routine blood glucose testing.
Also included in your initial consult is a thorough analysis of the above and a detailed report of findings. Then, according to your presenting symptoms and the results of your tests, a comprehensive health improvement plan tailored to your specific needs.
Request Appointment Online
Your customized health improvement plan…
Functional Health Report with recommendations and guidance for your specific health issues
All the resources you need to get well
Dysfunctions detected through science-based testing and analysis